Introduction
It is for this reason that injection moulding surface finishes can be said to be one of the most suitable manufacturing techniques for injection molded plastic parts in the current industrial sector. The surface finish of the injection-molded parts is an important aspect in as much as it can be a functional and visual determinant. Apart from cosmetic concerns, surface finishing influences the interaction, performance and cost of the part. This article covers all the topics related to the types of injection molding surface finishes possible, as well as enhanced finishing procedures and ways to address the frequent problems.
Understanding Surface Finish Importance

The surface finish of injection-molded part is not only a cosmetic notion for the sellers and buyers but has functional requirements too, including surface roughness . In the case of medical devices, it is advised that the surface should be smooth in order to inhibit bacterial buildup. Due to the textured surface of automotive application, the small defects cannot be seen and the scratches are not easily detected. In consumer electronics, the certain types of surface textures give consumers the sense of brand familiarity.
Surface finishes also affect functionality, including surface roughness ra . The right finish can:

- Reduce friction in moving parts
- Enhance grip for handheld devices
- Improve part release from molds
- Conceal purl lines, seam lines and other completed fabric imperfections
- Create light-diffusing or reflective properties
- Holes in the fabric that can be used to check how much resistance it has on fingerprints and smudges,_Time is taken in checking the fabric for difficulty in removal of fingerprints and smudges.
Standard Surface Finish Classification Systems

SPI/SPE Finish Standards
There is no standard system with a better acceptance than the one created by the Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) in the plastics industry. These indicate finishes by the codes A-1 portrayed by the highest polish and D-3 by the heaviest texture.
A Finishes (Polished): which are also referred to as spi finishes.
- A-1: Diamond buff (Ra 0-1 microinch)
- A-2: Paper polish (Ra 1-2 microinches)
- A-3: Stone polish (Ra 2-3 microinches)
B Finishes (Semi-polished):, which can also be categorized under spi surface finish.
- B-1: 600 grit paper (Ra 4-8 microinches)
- B-2: 400 grit paper (Ra 8-15 microinches)
- B-3: 320 grit paper (Ra 15-30 microinches)
C Finishes (Matte): which can include various textured surface finishes.
- C-1: Fine matte (Ra 30-45 microinches)
- C-2: Medium matte (Ra 45-60 microinches)
- C-3: Coarse matte (Ra 60-90 microinches)
D Finishes (Textured):
- D-1: Light texture (Ra 90-120 microinches)
- D-2: Medium texture (Ra 120-250 microinches)
- D-3: Heavy texture (Ra 250+ microinches)
International Standards

Although, the injection moulding process and the system of SPI standards prevail in North America and some other countries applied the other systems.
- The Mold-Tech explained above is an exclusive shape numbering system offering different textures.
- VDI 3400 : An European standard which is rated on a range of 0 (Polished) to 45 (Rough).
- Charmilles: A type of surface finish that is standard to Switzerland and is normally used for EDM surfaces.
- JIS of Japanese Industrial Standard is one of the most common standards utilized by the industry in Asia.
Factors Affecting Surface Finish Quality

Material Selection
It was indicated that various polymers behave in a way that is distinct depending on the applied plastic mold surface treatment.
- It was found out that non-crystalline polymers such as ABS, PC and PMMA in particular, yield smoother surfaces
- Two types of materials, namely semi-crystalline materials (PP, PE, POM) demonstrate a greater number of surface irregularities.
- The phenomenon increases surface roughness because of the presence of fiber protrusion in glass-filled materials
- Additives used in modifying the polymers may cause changes in the surface related to gloss and texture.
Mold Design Considerations

In terms of the surface finish, the mold machining plays a major role in achieving smooth finishes as well as textured plastic finishes masked chemical etching, doing the following:
- These are the aspects of the foundry gates that affect the flow pattern and most importantly the potential defects that are associated with them.
- Sufficient venting or venting adequacy helps to avoid formation of surface blemishes such as burn marks textured mold.
- This has an impact on an item surface flatness as well as avoiding sink marks formation mold polishing.
- Steel quality and hardness influence polish retention and durability grade c
- This paper analyzes the parting line placement’s implications for visible witness lines grit sanding stones.
Process Parameters

Pulse conditions affect the pencil hardness of HTS surface, which is related to texture depth typical surface roughness :
- Temperature farther influences the manner in which the material flows and replicates the surface of the tool fewer weld lines.
- Injection speed plays an important role in determining the extent to which the material covers the textured areas to a desirable level
- Thus, packing pressure controls the ability of material to conform to the surface of the mold.
- Since mass changes with speed of cool, shrinkage marks and surface crystallinity may be impacted dry blast 24 oxide.
- During mold temperature, there were reduction on material flow and surface gloss on the gate area as the platens move around for the next injection cycle fast injection speed.
Common Surface Finish Types
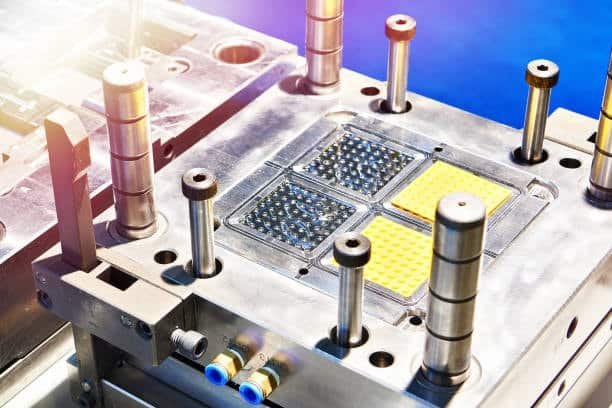

High-Gloss Finishes
High-gloss paints (A1 & A2) create smooth spi surface finish surfaces that are reflective such as a mirror and can significantly enhance paint adhesion, while also considering a semi gloss finish be attained by going through hardened tool steel:
- Diamond polishing of mold surfaces laser etching
- Multi-stage buffing processes high melt temperature
- Specialized mold steels with excellent polishability
- Careful material selection and processing
These are used in consumer electronics, cosmetics packaging, and high end automobiles due to their lustrous appearance plastic materials, however, they are susceptible to scratches, fingerprints and are difficult to be polished during manufacturing plastic injection molded parts.
Matte/Satin Finishes
Matte finishes (B and C categories) are less reflective and camouflaging small surface irregularities in the following ways:
- Controlled abrasive blasting of mold surfaces
- Chemical etching for uniform appearance
- Specialized bead blasting using certain size of bead
These finishes are typical for the functional parts, industrial equipment, and products where the traces of fingerprints spi mold finishes, and minor scratches should be concealed.
Textured Finishes
D categories, which are the textured surfaces vdi surface finish, have the following benefits:
- Leather grain for automotive interiors
- Wood grain for decorative elements
- Technical textures for improved grip
- Geometric patterns for brand identity
- The flow lines are often aligned and camouflaged using stucco finishes.
Specialized Finishes
During the recent decade, advanced manufacturing processes have emerged correlations for surface treatment:
- Soft-touch coatings for premium tactile feel
- Multi-component molding combining different textures
- In-mold decoration for complex graphics
- Hydro dipping for marbled or distorted patterns
Surface Finish Creation Methods
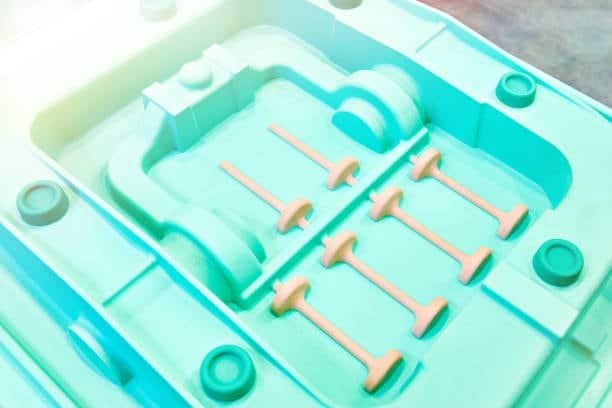

Mold Texturing Techniques
Chemical Etching
Chemical etching takes the form of photosensitive masks and chemicals therefore, possesses the following advantages:
- Excellent repeatability and consistency
- Ability to create complex patterns
- Ideal for curved boarded surfaces or any irregular shaped surfaces.
But of course, some drawbacks of this method are high cost for large surfaces and possible hazards connected with disposal of chemicals.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Shoulder EDM texturing utilizes controlled electrical discharges in order to effectively promote an eroding of specific surface forms.
- Creates precise, repeatable textures
- Works well with hardened steels
- Can produce unique spark-eroded finishes
EDM excels in reproduction of technical and analytical patterns but may also include higher costs and amount of time spent.
Laser Texturing
Laser texturing is a method, which utilizes beams of light to adjust certain characteristics:
- Produces very accurate pattern and printing that has a very close mesh.
- Offers excellent reproducibility
- Allows the formation of micro-textures that can’t be produced by conventional techniques
The last type of layout is more complex but is brilliant to execute; however, it has to be done by a professional equipped with the appropriate machinery.
Direct Machining
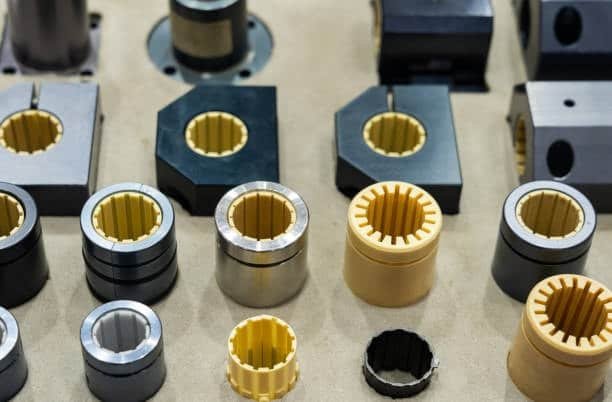

CNC machining in a way directly scratches various shapes of patterns on the surface of molds.
- Straight-line textures and geometric patterns
- Ball end mills produce the following types of finishes:
- Custom engraving capabilities
Good control is sometimes provided by this approach; however, it is unsuitable for analysis of complex organic structures.
Post-Molding Surface Treatments
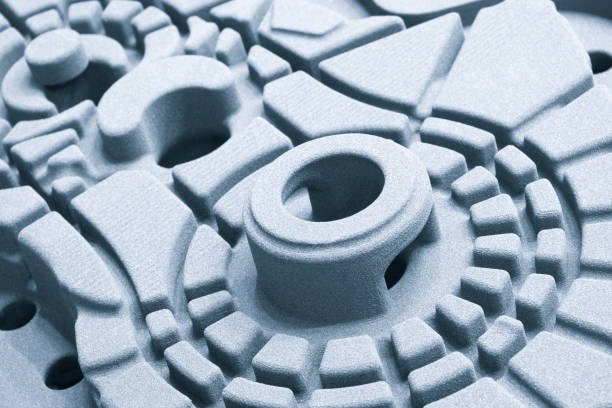

Media Blasting
The developed pieces need treatment with multiple blasting materials.
- Glass beads for satin finishes
- Aluminum oxide for more aggressive texturing
- Walnut shells for gentle surface modification
Tumbling and Vibratory Finishing
Mass finishing techniques include:
- Products move inside an enclosed barrel to receive burr removal treatment and softened edges.
- Vibratory finishing videos parts to achieve specific surface smoothing requirements.
- Using Centrifugal disc finishing lets us reduce processing time.
Coating and Painting
Surface coatings improve the performance of injection moldings by adding quality improvements, including a glossy finish .
- A paint spray application brings color choices and textural changes to parts.
- Soft-touch coatings for premium feel
- UV-curable coatings for durability
- Anti-fingerprint treatments for high-touch surfaces
Selecting the Appropriate Surface Finish
Functional Requirements
Function should guide finish selection:
- Parts exposed to heavy usage need textured designing to resist scuffing
- Parts with movement need defined slippery and sticky areas
- Medicine requires smooth surfaces because they need to remain clean
- Outdoor applications need UV-stable finishes
Aesthetic Considerations
Brand identity and design patterns determine our choice of surface finishes
- Consistency across product lines
- Premium vs. utilitarian appearance
- Visual harmony with other materials
- Light reflection and diffusion properties
Manufacturing Implications
Actual production needs determine the right finish to use
- Advanced surface treatments raise mold spending and upkeep expenses
- Most polished parts take longer to finish production.
- Part release may suffer from choosing particular surface treatments.
- Part textures help disclose or make less visible production flaws.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Financial considerations include:
- Initial mold investment vs. part lifespan
- Maintenance requirements over production runs
- Organizations determine scrap levels linked to their product coatings
- The desired outcomes need additional processing steps to achieve them.
Common Surface Finish Defects and Solutions

Flow Marks
Flow marks develop as surface undulations because of these three issues:
- Uneven cooling during fill
- Improper gate location
- Insufficient injection pressure
Solutions include:
- Optimizing gate location and size
- Increasing melt and mold temperatures
- Adjusting injection speed profile
- Placing texture over the affected area can hide the problem
Sink Marks
The dense portions of the model reveal themselves as sunken spots because of these problems.
- Uneven material shrinkage
- Insufficient cooling time
- Inadequate packing pressure
Remedies involve the use of dry blast glass bead techniques.
- Modifying the design to make the part wall sections equally thick
- Increasing packing pressure and time
- Optimizing cooling system design
- The placement of textured areas helps cover small sinking mistakes in the casting design
Weld Lines
Weld lines appear at the contact point between two flowing plastic streams and often display these signs:
- Visible lines on the surface
- Color variations at the junction
- Structural weakness
Manufacturers use various methods to reduce weld lines in their products, paying close attention to eliminating tool marks that can affect surface quality .
- Our focus is to arrange gates better in the mold for smoother material movement.
- Increasing melt and mold temperatures
- The correct surface texture hides evidence of appearance issues
- Control the venting system at points where weld lines appear
Orange Peel
The skin of orange peel does not appear smooth because it develops dimples that resemble actual citrus surface texture, which can also increase weld line visibility as described in the description applications surface roughness.
- Improper material drying
- Inconsistent mold temperature
- Incompatible material and process conditions
Corrections include:
- Following correct material treatment before drying
- Stabilizing mold temperature
- Adjusting injection speed and pressure
- Examine and test other materials that help substances move more easily
Polishing Issues
Surface polishing problems include several factors which create challenges.
- Diamond polishing produces the best possible polished results in practice
- Direction consistency during polishing operations
- Mold steel selection for polish ability
- Regular mold care protects the surface appearance of finished parts
Advanced Surface Finish Technologies
Micro-Texturing
The texturing process makes very small surface designs that achieve these effects.
- Enhance hydrophobic or hydrophilic properties
- Create self-cleaning surfaces
- The small-scale surfaces of the material need reduced friction to work correctly.
- Improve optical properties
Multi-Material Surface Finishes
Modern injection molding enables:
- Manufacturing combines multiple materials to produce multiple surface textures.
- Hard/soft combinations for ergonomic benefits
- Transparent over opaque materials for visual effects
- The process connects seal elements directly to fixed parts during production
Smart Surfaces
Emerging technologies include:
- Touch-sensitive surfaces integrated during molding
- Antimicrobial additives for healthcare applications
- Self-healing polymer surfaces
- Color-changing materials responding to temperature or UV
Sustainability Considerations
Environmental Impact
Surface finish choices affect sustainability:
- Manufacturing items with premium polished surfaces needs additional energy and processing materials.
- Some texturing products create environmental problems.
- Product life span and recycling capabilities depend on finish life span.
Recyclability Factors
Surface options impact the ways products can be processed when reaching the end of their life.
- Some coatings complicate recycling processes
- Surface-effect components with specific additives often make recycling more difficult.
- One-piece materials help items get recycled easier.
Industry-Specific Surface Finish Requirements
Automotive Applications
Automotive components require specialized considerations:
- UV resistance for exterior components
- Product designers use antireflection surfaces to lower dashboard shine.
- Scratch resistance for high-touch areas
- Consistent textures across multiple molds and production runs
Medical Device Finishes
Healthcare products demand specialized surfaces:
- Biocompatible finishes for patient contact
- Smooth surfaces for infection control
- Chemical resistance for sterilization procedures
- Clear documentation for regulatory compliance
Consumer Electronics
Electronic devices utilize finishes for:
- Brand differentiation through signature textures
- Fingerprint resistance on high-touch surfaces
- Heat dissipation enhancement
- Improved grip for handheld devices
Future Trends in Injection Molding Surface Finishes
Digital Surface Design
Emerging technologies include:
- We generate textures using algorithms that match product requirements
- Digital twins of surface textures for virtual testing
- AI-optimized surface patterns for specific performance criteria
Advanced Simulation Tools
Modern software enables:
- Prediction of surface defects before mold creation
- Our system evaluates how texture changes the product response during production operations.
- Digital systems test surface appearance effects under all lighting options
Nanotechnology Applications
Future developments will likely include:
- Nano-textured surfaces with specialized properties
- Self-organizing surface structures during molding
- New materials adopt natural structures from the living world
Conclusión
Selecting surface finish choices for injection molded parts includes weighing many factors between appearance needs, functionality standards, production capabilities and budget allocation. Manufacturers now produce an array of fine patterns from simple polish to micro-level product enhancement to better meet modern buyers’ specific needs.
Manufacturing improvements in injection molding materials will help us build better surfaces that improve product functionality alongside beautiful designs and use fewer resources. Companies that know how to select surface finishes achieve better market success because of their improved products and streamlined production methods.

