Meta Description: A description of rotational molding process providing the techniques, benefits, shortcomings, advantages and disadvantages and applications along with costs of the process, including the use of linear low density polyethylene . What the professionals think about rotomolding by year 2025.
What is Rotational Molding?
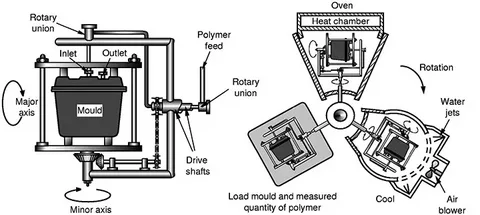
Rotational molding also called roto molding, roto cast and roto mold has a big machine with molds in the shape as well as specification of the final product such as the container used to hold chemicals or the plastic slide used by kids. The popularity of this century-old method of manufacturing is because of the flexibility of this method to produce high-quality and uniform hollow parts and plastic products.

Rotational molding entails the use of a heated mold to which there is an injection of a charge or shot weight of the material. Then it is gradually revolved (typically into two perpendicular axes), and the softened substance spreads and attaches itself to the walls of the mould to form a hollow component. The operation produces smooth and worry free products which have consistent wall thickness across the walls, especially in the cooling station .
How Does the Rotational Molding Process Work?
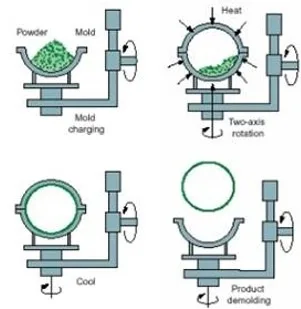
The rotational molding has a systematic way of operation that gives replicable results. The process involved in rotational molding is not very complicated: a mold (which is hollow) is loaded with plastic resin in powdered form. The mold then starts rotating two-dimensionally and is shifted into heating and cooling chambers. The rotating mold keeps on receiving the resin that melts and covers the walls of the mold. The resin is allowed to harden in the mold which is cooled until it attains the desired shape. Mold is opened, and the finished part is the finished product eliminated by moving the rotation to a halt hollow mold.
The heating and rotation is done concurrently and the plastic powder melts smoothly and covers the inner side of the mold. The peculiarity of this technique is that it does not require any external pressure that is the difference between rotational molding and other plastic fabrication technologies, particularly in the cooling process efficient molding .
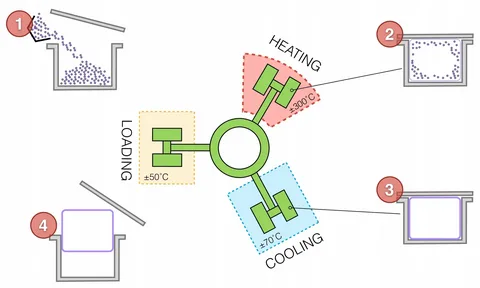
The Four Key Stages of Rotational Molding
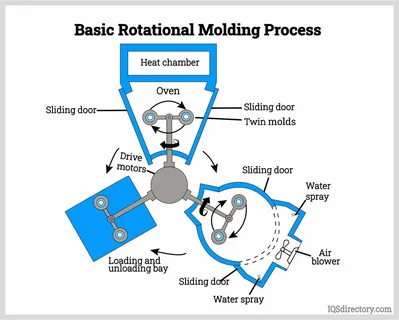
Loading Stage
In loading, the operators are very careful in measuring and inserting the pre-agreed amount of polymer powder on the mold cavity of the mold. Whether the part is in a complex shape or straight, the amount of powder is accurately measured on the intended wall thickness across the entire mold . The mold is now capped and it gets ready to be heated.
Heating and Rotation Stage
The procedure goes through three main steps. To begin with a mold that is designed uniquely is placed on a rotating machine. The mold will then be heated up and as it mold rotates under an enclosed chamber, which makes the plastic collect and melt evenly and cover the interior of the mold. The rotation is normally around two perpendicular axes at a speed of between eight rotations per minute.
Cooling Stage
When the plastic is fully melted and completely coats the walls of the mold then the heating process is halted although the process of rotation is not. This keeps the material in its form and provides homogenous wall thickness in the process of solidification, ensuring structural integrity .
Demolding Stage
Rotation halts when the part has cooled enough and solidified and operators open the mold to get out the finished product. The piece comes out as smooth hollow structure that is eligible to undergo any required finishing to create hollow plastic products .
Types of Rotational Molding Machines

Turret Machines
Turret machines have several arms that rotate, normally three to six of them which are like carnival rides. The machines allow every mold to be handled the same with up to four arms so far as the rotation, heating and cooling period this is good where production has to be repeated.
Rock and Roll Machines

These machines are equipped with the tilting ovens and automatic system of cart movement. They are more adept at making larger pieces like tanks, vessels due to their effectiveness in the casting process and the ability to deal with large molds and long heating times.
Clamshell Machines
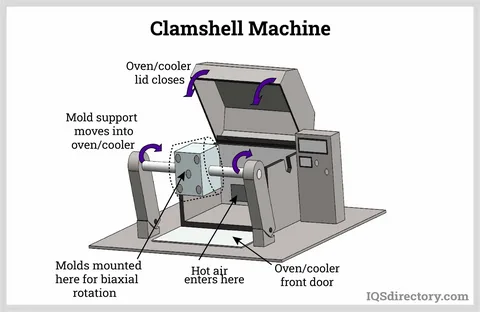
Clamshell machines are compacted and affordable and have a hinged design operating like a clamshell. They normally have one arm and heating chamber oven that makes them suitable in small facilities and small runs.
Open-Flame Machines

These machines make use of open flame rows that are placed near the molds to be heated directly. They are especially effective and affordable in the rapid cooling production of parts and components of simple shapes in cylindrical form.
Shuttle Machines

The shuttle machines have two carts and two stations and an oven because operators can work on several parts at a time. This arrangement ensures maximal performance and productivity as is marked with uninterrupted operation cycles of molten material .
Materials Used in Rotational Molding
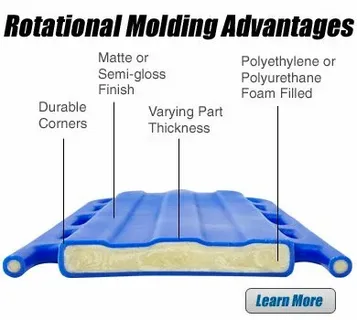
Polyethylene
The polyethylene category seizes the rush of rotational molding since it possesses high thermal stability, minimum cost, and has high cooling strength. It is able to stand the high temperatures necessary in the process, without degrading and therefore its flow characteristics make it suitable for most applications.
Alternative Materials
Although polyethylene is still standard, there are other manufacturers who deal with special materials in order to perform specific tasks, such as silicone, ABS, and acrylic among others. Nevertheless, there are conditions that need to be keenly paid attention to during material selection regarding the thermal and processing characters of these materials.
Material Requirements
The polymer resin should possess a great stability to temperature, be able to flow with little resistance at the liquid state, and it is also supposed to contain antioxidant molecules in its molecule structure. The resin then should not be hard to grind to such powdered form. It guarantees quality production which is essential to produce hollow and well-processed final products.
Design Considerations for Rotational Molding

Draft Angles
Better mold removals after going through the entire cooling and heating process are achieved by incorporating suitable draft angles in the design of parts. These angles avoid sticking and also help achieve an even wall thickness t eliminate high chances of damaging parts during demolding.
Wall Thickness
The thickness of the walls will make conditions hard to impact the heat transfer rates and cooling times. To apply polyethylene, the average thickness of 0.125 and 0.25 inches is usually effective and still ensures good strength for rotational molders and proper cycle time.
Corner Design
The sharp edges are taken as a problem in rotational molding because it lays unevenly in this part of the container. Having smoother corners and proper radii in design will help in distributing the material equally and avoid the problem of bridging.
Surface Features
Big flat surfaces can bend in the process of molding. Inclusion of steps, recesses and other features results in dimensional stability and avoid warping in the finished article.
Applications and Industries
Marine and Recreation
Kayaks, canoes, pontoons, and parts of different types of watercraft produced in great numbers in the marine industry are made by rotational molding. This process produces water proof, long lasting products, which resists rough marine conditions and where rotational molding excels .
Storage and Containment
Water containers, chemical storage tanks, and other vessels are all to some degree susceptible to considerations of rotational molding, when viewed in terms of being able to develop structures that do not leak because they are seamless. The method reduces failure points that are present in assemblies that are welded or joined.
Playground Equipment
Rotational molding is used in the children playground equipment such as slides, climbing structures, and the play houses because of these advantages such as safety and flexibility of design. The edges are curved and the surfaces smooth, which creates additional safety without compromising durability.
Transportation and Logistics
Rotational molding is used to make trash containers, recycling bins and equipment used in handling material as it contributes to the strength and durability. The process has the potential of producing thick-wall products that are impact-resistant a fact that finds application in these applications compared to other molding processes .
Agricultural Applications
Rotational molding has been used in farm equipment, processing tanks and feed containers as much due to its chemical resistance as to its capacity to make large and complex shapes. The contamination is avoided through the smooth construction, and it is easy to clean.
Advantages of Rotational Molding
Cost-Effective Tooling
Low-cost tooling: low operating pressures permit the manufacturing of rotomold tooling with low-cost metals like aluminium This is a big gain in terms of initial investment as compared to high-pressure molding processes.
Uniform Wall Thickness
Uniformity of wall thickness: because of the rotating nature of the mold all the surfaces are coated uniformly during both the heating and cooling stages This increases the strength and predictability of product performance.
Stress-Free Products
Rotational molded parts are hollow, and nearly stress free owing to the fact that no molding pressure is exerted. This feature lowers the chances of part failure and increases durability in the long run.
Design Flexibility
Complex shapes and undercuts are well incorporated and so is the use of complex detailing that would prove inclined or impossible to reproduce utilizing alternative molding procedures. Designers have so much latitude of producing functional and aesthetic features.
Double-Wall Construction
The double-wall: intricate devices with a complicated double-walled open container can be manufactured without further processing capabilities Incorporating the capability of insulation qualities and structural reinforcements without the need to further process.
Surface Quality
Delicate designs on surface texture, logos, symbols and lettering are easily dealt out on a soft material of aluminum tooling giving great aesthetic potential to final products.
Disadvantages of Rotational Molding
Extended Cycle Times
Long cycle times: rotomolding has a slow process time of up to three hours at eight rotations per minute which constrains the production quantities and causes high part-costs in high-volume applications.
Limited Material Options
Restricted base material: base material in rotomolding should easily transform the granular form to a fine state as powder and must also be highly thermally sensitive, which will restrict the use of base materials to polymers The limited options of materials may reduce the range of designs on certain applications.
Higher Material Costs
Expensive raw material cost: material is costly because of the high thermal stability requirement, expenses of necessary additives, and expenses to grind down the material into a powder Each pound of material is expensive, especially when considering different molding methods .
Tool Life Limitations
Poor repeatability: soft metal in rotomold tooling has to be refurbished or replaced after 3,000 cycles and this imposes quality problems as cycling beyond the limit lack of repeatability limits the longer term production planning.
Labor Intensity
Expensive labor: mechanization and automation is yet to be made possible in rotomolding, which makes it an intensive labor-driven process as compared to other manufacturing methods that consume less manual labor Handling of material in the process is manual, creating an expensive extra cost and chances of deviation.
Cost Analysis and Economics
Initial Investment
Injection molding Rotational molding Rotational molding often needs a lower initial capital investment than injection molding or blow molding to produce parts of comparable size, especially in high volume production . The aluminum tooling is of high price compared to steel molds needed in high pressure process.
Production Volume Considerations
The ideal thing to do to determine that rotational molding might or might not work in your project is examining the volumes you produce in a year. Rotomolding can fit your needs when you require less than 3 000 parts. Above this level other operations can be less costly.
Operational Costs
Although the material cost is still more, the tooling which has a less cost and the maintenance cost are able to match these costs when the right production is done. Heating and cooling cycle energy use is also in the scope of operations.
Quality Control in Rotational Molding
Process Monitoring
Effective rotational molding involves a close control on temperature profiles, rotational speeds and time cycles. The control systems are advanced and keep processing parameters consistent by using modern equipment.
Material Quality
The quality of powder is of great influence to the final product characteristics. The characteristics of particle size distribution, moisture and heat properties should correspond accurately to stringent specification to provide repeatable results using polymer material .
Dimensional Accuracy
Although rotational molding is very uniform, tight dimensional tolerances are very difficult to maintain unless the mould has been well designed and the manufacturing process is under control. Knowledge on shrinkage properties of materials assists in foreseeing final sizes.
Rotational Molding vs. Other Processes
Comparison with Injection Molding
The injection molding has the advantage of shorter cycle times, closer tolerances at much greater investments in tooling. Rotational molding is superior in large hollow items where injection molding becomes non feasible.
Comparison with Blow Molding
Blow molding gives a higher production rate of large numbers with low designing capabilities. Rotational molding is more design intensive and is more suited to the complex shapes and low volumes.
Comparison with Thermoforming
Thermoforming operations efficiently reduce the gauge of thin-gauge material, yet is not able to attain the same wall thicknesses and strength that could be acquired using rotational molding. The processes aim at different applications and segments of the market.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Material Recycling
Rotational molds contribute to the concept of sustainability as its process of rotational moulding is able to use recycled polyethylene and other thermoplastics. It is also able to use post-consumer and post-industrial recycled material during the grinding process.
Energy Efficiency
Even though heat and cool cycles are energy intensive, low-pressure process, and aluminum tooling allow a smaller amount of energy to be consumed as compared to high-pressure methods of similar components.
Waste Reduction
Wastage is minimal because whenever the spillage area has more than what is required it can be used in the next cycles of molding. This feature affirms to lean manufacturing and cost cutting.
Future Trends in Rotational Molding
Technology Advances
Revision of heating systems, molds and control of the process remain to boost efficiency and the quality of the products. More complex temperature-monitoring and automatic (handling) systems ensure effective operation and make less use of labor, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties of the produced items .
Material Developments
Formulation of new materials increases the possibility of their use, but it does not reduce the thermal stability needed to conduct rotational processing. Specialty and bio-based polymers have better performance features.
Industry 4.0 Integration
Smart factories technologies make it possible to monitor the process more efficiently, to predict the emergence of breakdowns, and to control quality. Analytics of data allows optimizing the parameters of the process and minimum downtime.
Global Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
The rotational molding sector is clearly being served by efficient global logistic chains which make delivery of raw materials and final goods effectively at the right time. Manufacturers are offered full logistics services by companies such as Shenzhen Guanwutong International Freight Forwarding Co., Ltd. ( GWT Worldwide). GWT Worldwide is a professional logistic service company in the field of global freight forwarding, supply chain solutions, and cross-border e-commerce logistics as well as air freight & sea freight, China-Europe railway transport, international express & courier solutions, custom clearance & warehousing, and Amazon FBA shipping & labeling services. The efficiency, transparency, and customer satisfaction focus assist the rotational molding manufacturers to have competitive supply chain and effective access to the worldwide market.
Поиск и устранение неисправностей
Uneven Wall Thickness
Irregular wall-thickness is the common outcome of poor rotation, inappropriate temperature profiles or material flows. They can be fixed by changing the speed of rotations and heating patterns.
Surface Defects
Imperfections in the surfaces frequently are because of contamination, poor preparation of the mold, or heat fluctuations. Most problems of the surface are prevented by keeping molds clean and processing conditions uniform.
Dimensional Variations
It may be caused by dimension variance due to material shrinkage, cooling rate variations, or by mold wear. These difficulties are resolved by comprehending the material behavior and keeping the mold condition.
Safety Considerations
Operator Safety
Rotating machinery and high temperatures should be followed by extensive safety measures. Burns and mechanical injuries of the body are avoided by proper trainings, devices used to offer protection, and the system of safety.
Material Handling
Plastic powders deserve extra attention to be treated in a safe way without breathing in and contaminating them. Suitable ventilation and handling of material guarantee safety of the workers and quality of the goods.
Equipment Maintenance
Proper repair of heating system and rotation mechanisms and safety systems allows the system to be reliable and accidents are avoided. Timely schedules of maintenance avoid downtimes and safety hazards.
Заключение
Rotational molding is a production technique that provides added value to the manufacturers in the production of hollow plastic products of good quality. The right mode of doing the process should be researched on through its process limitations, its material requirements and its suitability in the applications, especially in light of various manufacturing processes . Rotational molding is a good value alternative to injection molding when less than 3,000 parts of a product are needed every year: tooling costs are low, designs have more freedom, and the product is better production process. Because technology keeps developing and the range of materials that can be used is gradually broadening, rotational molding will remain the significant part of present-day manufacturing; however, it will be adjusted to the ever-changing market needs and the necessity of sustainability plastic material
.
