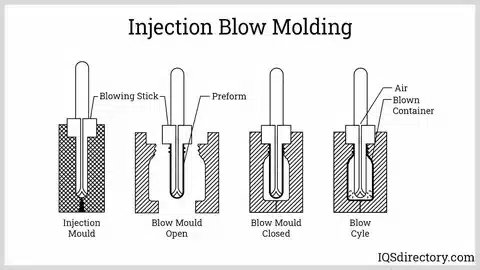
Introduction: The Battle of Molding Techniques
The products we use every day are molded by the use of molding, whether the item is the bottle in your hand or a part of your car. However, when is it better to use blow molding, rather than injection molding? The two manufacturing processes of plastic have transformed the way we fabricate everything in medical equipment or consumer packaging, but they have totally different functions in contemporary manufacturing.
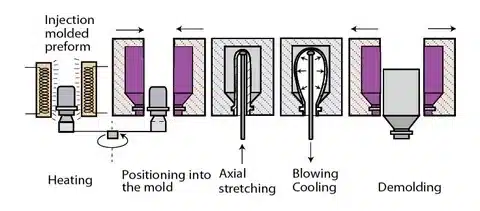
This full-scale guide will help you know the differences between these two manufacturing processes and also help you choose which method best suits your product requirements. As a product designer, engineer, or business owner trying to find out the options to manufacture a product, it is important to know these plastic molding techniques to make a sound decision that will not only affect the quality of the product but also its cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the Basics
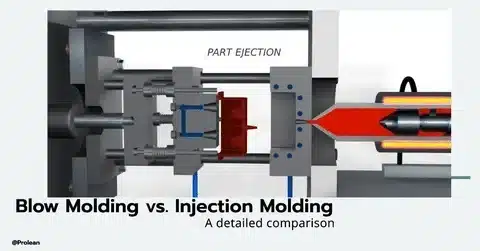
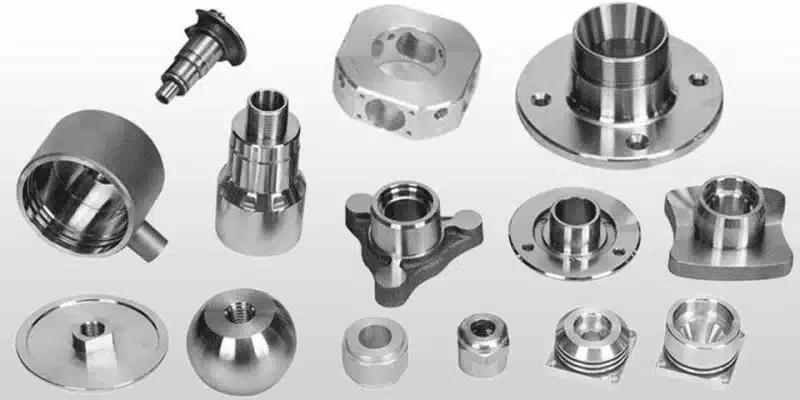
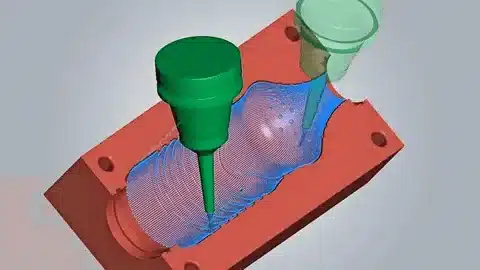
Injection Molding is a production technique that involves the high-pressure injection of the hot liquid plastic into a closed mold cavity. When the plastic is allowed to cool and solidify, the mold is opened to show a fully solid part. This process is best in the production of complicated geometries with narrow tolerances and high-quality surface finishes.
Blow Molding is a process where hollow parts are made by inflating a mold cavity with compressed air through a molten tube of plastic (also known as a parison) into the cavity. The method involves heating plastic resin to make it malleable, then subjecting it to an expansion of air pressure to make the required hollow shape.
Key Differences at a Glance
Part Geometry
- Injection molding: Molds solid components with complex design, detailed features, and assemblies of more than one component.
- Blow molding: In this method, hollow, thin-walled components of uniform thickness of the walls without crevices are made.
Material Usage
- Injection molding: Suitable for thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers with a wide range of material capabilities.
- Blow molding: Thermoplastics (polyethylene, PE, polypropylene, PP, and polyethylene terephthalate, PET) are largely used.
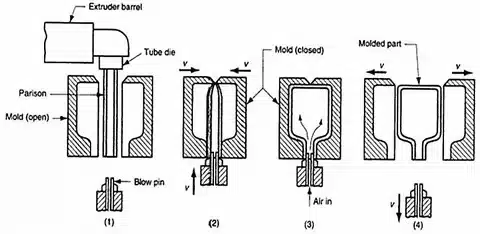
Tooling and Equipment
- Injection molds: More complicated and costly because of complicated cooling systems, ejection systems, and accuracy.
- Blow molds: The simplest to build and often cheaper, with simple designs of cavity and simple operation.
Production Speed
- Injection molding: Can achieve shorter cycle times on solid parts, where there is optimization of the cooling system.
- Blow molding: It is very effective in a high-volume production of hollow pieces, and simple geometries have a fast cycle time.
Pros and Cons Comparison

Injection Molding Advantages
- High precision and repeatability: Delivers narrow tolerances with stability through production cycles.
- Complex part capability: Produces detailed designs, undercuts, threads, and in multi-material combinations.
- Excellent surface finish: Provides smooth and high-quality surfaces with minimal post-processing.
- Material versatility: Supports a broad range of plastic materials and additives.
Injection Molding Disadvantages
- Higher initial tooling costs: Multifaceted molds are costly to invest in.
- Not suitable for hollow parts: Lacks big hollow structures.
- Longer lead times: The time taken in designing and making tools may lengthen project times.
- Higher per-part cost for low volumes: Economics prefer high-volume production.
Advantages of Blow Molding Over Injection Molding
- Cost-effective for hollow parts: This is the best solution when containers, bottles, or hollow structures are required.
- Faster production cycles: Effective manufacturing in the case of certain products.
- Lower tooling investment: Molds made it easier to save on start-up.
- Seamless hollow construction: Constructs hollow parts that are strong and without weak joints.
Blow Molding Disadvantages
- Limited to hollow, thin-walled parts: Not capable of producing solid or complicated geometric
- Post-processing requirements: Can require trimming to eliminate extraneous material (flash).
- Material limitations: Limitations are mainly on thermoplastic materials.
- Design constraints: Few design capabilities in terms of making complex internal features.
When to Choose Which?
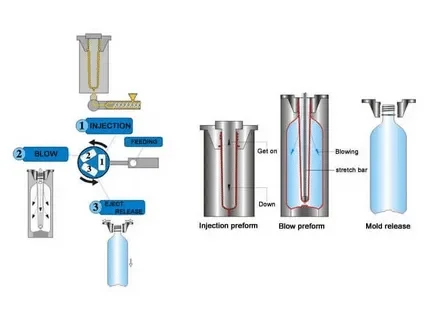
Opt for Injection Molding When:
- Manufacturing components of solid material with complicated designs and intricacies.
- Applications that demand high strength, durability, and dimensional precision.
- Production of multi-component assemblies or overmolded components.
- Production of high-accuracy parts in the automotive, medical, or electronic industry.
- Special materials or additives.
Opt for Blow Molding When:
- Producing hollow products such as bottles, containers, and tanks.
- The focus of product design revolves around cost savings in the materials and weight minimization.
- Hollow part production in large volumes with simple geometries.
- Production of hollow structures based on seamless structures that do not require assembly.
- Working with conventional thermoplastic.
Real-World Applications

Injection Molding Examples
- Automotive components: Dashboard components, internal components, engine parts, and electronic components.
- Medical devices: Syringes, surgical equipment, diagnostic equipment casing, and prescription administration equipment.
- Consumer electronics: Smartphone cases, computer keyboards, appliance covers, and connectors.
Blow Molding Examples
- Packaging solutions: Water bottles, food bottles, cosmetic bottles, and pharmaceutical bottles.
- Automotive parts: Fuel tanks, air ducts, and fluid tanks.
- Industrial containers: Chemical storage tanks, agricultural containers, and large-capacity drums.
Cost Considerations
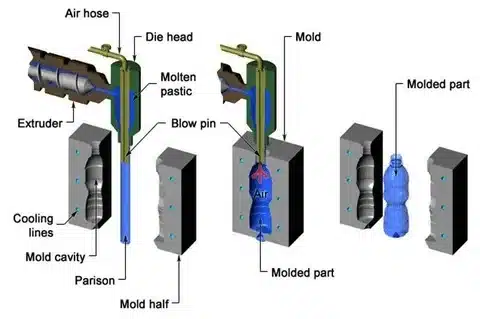
Cost Comparison Between Blow Molding and Injection Molding
Injection Molding Costs:
- Increased initial investment, as a result of the intricate design of molds and finer machining.
- Depending on complexity, the prices of tools may be in the range of 10,000 to 100,000 and beyond.
- Reduced per-unit costs realized in large volumes of production (usually 10,000 or more parts).
- Other secondary operations and assembly costs as and when needed.
Blow Molding Costs:
- Lower start-up cost and less complicated mold construction.
- Most applications have a range of tool costs between 50,000 and 5,000.
- Low cost when large volume hollow parts are required.
- Less waste of material than machining solid parts out of stock.
The break-even point among processes is based on the volume of production, the complexity of parts, and the application requirements. Blow molding is generally more economical for hollow components, and injection molding is more economical for complex solid parts.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Product
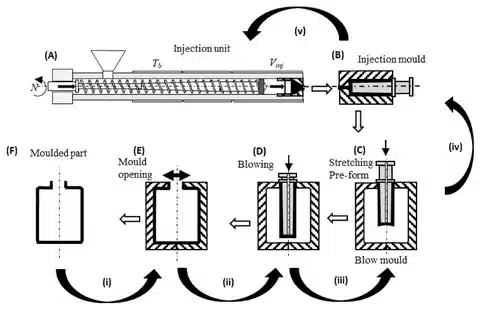
Critical Factors to Consider
Part Complexity and Geometry: Is your design a solid construction with complex detail (injection molding) or a hollow, simple shape (blow molding)?
Production Volume Higher volumes will tend to prefer injection molding on complex components, but blow molding will be cost-effective over a wide range of volumes on hollow products.
Material Properties and Requirements: Take into account material compatibility, performance requirements, and special additives or properties requirements.
Budget and Timeline Constraints Balance initial tooling costs and per-part expenditures versus Project timeline requirements.
Decision Flowchart
- Is your part hollow? – Yes: Take into account blow molding – No: Take into account injection molding
- Does it involve complicated geometry? Yes: Yes: Injection molding No: Yes: Evaluate volume and cost
- What is your volume of production? – High volume + simple geometry: Blow molding – High volume + complex: Injection molding
- How much do you budget for tooling? – Low cost + hollow component: Blow molding – More expensive cost + complex need: Injection molding
Conclusion
Whether to blow-mold or inject-mold is, it is a matter of your choice, the product you are dealing with, volume of production, and budget. Another reason why injection molding is the most suitable option in the production of complex solid parts that are also highly precise, besides the flexibility of the type of material, it has been an ideal fit in the production of parts that are auto parts, medical equipment, and other complex consumer products. Blow molding is more economical when dealing with hollow parts like bottles and containers, and offers cost-effective solutions where there is less tooling investment and production cycles are cost-effective. Understanding the advantages of blow molding over injection molding, particularly in hollow products, and contrasting the cost of the blow molding and injection molding processes will aid you in making the most suitable decision on the manufacturing process to be applied. Determine what your specific needs are, possibly your part geometry, volume to be produced, material needs, and budget limitations, and seek the counsel of seasoned manufacturing professionals who can provide a detailed analysis and solution to your special needs based on the project.