Introduction
Do you realize that your water bottle that you drank this morning and your polyester shirt are probably the same basic substance? PET plastic, which is used in beverage containers and the fibers of clothes, has become one of the most widespread substances in the current society. Since consumers are increasingly aware of environmental impact and sustainability, no time could be more crucial in learning to understand this versatile polymer. This is a complete guide on the nature of PET plastic, its characteristics, uses, advantages, disadvantages, and the significant part it plays in our everyday lives as well as in the environment in our future.
What Is PET Plastic?

PET is the abbreviation of Polyethylene Terephthalate, which is a polymer resin that is thermoplastic in nature within the polyester family. This is a synthetic substance, and one of the most significant plastics in world production, whose recycling code is number 1, and which is characterized by its amazingly versatile applications in a variety of fields.
PET plastic chemically consists of two main elements, which are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, that are polymerized. These molecules combine by means of a condensation reaction process to produce long chains of polymers that give the unique properties to PET. This is the molecular structure that makes PET plastic of such impressive qualities as high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and superior clarity, comparable to glass.

PET plastic has a number of major properties that render it invaluable in a number of applications. It has a higher strength-to-weight ratio of strength to weight than many conventional materials, and the material is flexible and has impact resistance. The material has high barrier qualities to gases and moisture, and this makes it the best in preserving the quality of products. Moreover, PET plastic is clear and glossy and has aesthetic value in packaging, while being fully recyclable.
Common Uses of PET Plastic

Packaging Applications
PET plastic has found its way to the packaging market, especially in drinks containers, where it has been estimated to have a 70 percent market share across the world. PET has a great ability to retain the freshness and safety of products because water bottles, soft drink containers, and juices depend on the high-quality barrier properties of PET. Ready-meal trays, salad containers, and bakery packaging are the areas of application in food packaging where PET is applied because of its clarity, allowing consumers can look at the contents without any chances of contamination.
Another important use of PET plastic is thermoformed packaging; the thermoformed package is used to produce blister packs of pharmaceutical products, electronic packaging, and display containers in shops. This is due to the capacity of the material to be heated and molded to accurate shapes, making it irreplaceable in packaging solutions, which are tailor-made to fit industries.

Textile Industry
PET plastic is made into polyester fibers in the textile manufacturing process by spinning it into one of the most popular synthetic fabrics in the world. The recycling of PET plastic is also used by clothing producers to create ecological polyester products out of recycled waste, which enhances the idea of the circular economy. PET-based polyester is often used in home textiles (e.g., carpets, upholstery, and bedding) due to its durability and easy-clean characteristics.
Other Applications
In addition to packaging and textiles, PET plastic finds a variety of special-purpose uses by various industries. The uses of PET in medical device manufacturing are surgical implants, medical tubing, and the housings of diagnostic equipment because of its biocompatibility as well as resistance to sterilization. PET has a temperature resistance and dimensional stability that is beneficial in automotive parts such as interior parts and generally under-hood applications. Circuit boards, display panels, and protective housings used in electronics manufacturing use PET plastic in their manufacture because clarity and electrical characteristics are critical in such applications.
Advantages of PET Plastic

Durability and Performance
PET plastic is extremely durable and is resistant to impact, which can break up glass substitutes; however, it resists impacts with a high level of structural integrity. It has a moisture-resistance property that prevents it from degrading in wet environments and, hence, is applicable in outdoor performance and long-term storage. PET plastic can operate in a wide range of conditions because of its temperature stability, which can be frozen food packages or hot-fill beverages.
Aesthetic and Functional Benefits
PET plastic has spectacular transparency, and the crystal-clear view of the product is the best marketing feature because it stands out and is accepted by customers in the retail market. Its high gloss surface finish provides a high look, and it does not scratch or cloud. Lightweight products lower transportation expenses and energy use, and still provide similar strength to heavier products.
Environmental Advantages
The most notable advantage of PEET plastic, as far as the environment is concerned, is that it can be recycled entirely. PET can also be recycled in a closed-loop many times and does not lose much of its quality due to recycling, which is compatible with circular economy principles. Recycling needs less energy as compared to virgin PET production, and has decreased the total carbon footprint. Further, recycling PET plastic can be used to replace new materials in many applications, saving natural resources and decreasing the amount of waste.
Disadvantages of PET Plastic
Environmental Concerns
In spite of the benefits of recyclability, PET plastic brings up some environmental issues when not handled properly. The non-biodegradable character of the material implies that the material remains in natural environments for hundreds of years unless it is recycled. PET bottles and containers can cause ocean pollution, which causes harm to the marine ecology and wildlife, and food chains. The formation of microplastics based on degrading PET materials finds its way into water supplies and food systems, and this poses possible long-term environmental impacts.

Health Considerations
In some circumstances, the plastic used in PET can leak trace elements of chemicals especially when using in high temperatures or in the ultraviolet radiation in the prolonged use. Although regulatory authorities typically accept the use of PET as food contact safe, there may be an issue of antimony and acetaldehyde (anticorrosion) migration through the packaging into the food. PET bottles used on a single occasion can be contaminated by bacteria in case they are reused without being cleaned, and this is damaging to their health.
Recycling Limitations
Contamination greatly affects PET plastic recycling efficacy because food waste, labels, and mixed substances are difficult to process. Color differences within PET containers pose a difficulty in the formation of clear recycled material, which restricts its use in the end. The technical feasibility of PET plastic recycling does not translate into actual high recycling since many areas have infrastructure constraints to support its collection and processing.
The Manufacturing Process of PET Plastic
Polymerization Process
The manufacture of PET plastic commences with the polymerization stage, in which the ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid are subjected to a condensation reaction involving a temperature that is above 250 °C. The process forms polymer chains of definite molecular weights that define the properties of the end material. The reaction is catalyzed, and the stabilizers ensure the process is not degraded during processing. The resulting PET resin is in the form of small pellets that can be processed further into an end product.

Shaping and Forming Methods
The most popular way of producing PET plastic products, especially containers and packaging parts, is injection molding. It is done by heating PET pellets until they melt and injecting the material into high-pressure, precise molds. Temperature and pressure regulation assure a good orientation of the molecules and the best material characteristics.
An Extrusion process is used to form continuous plastic profiles, sheets, and films of PET by pumping a molten feedstock through predefined shaped dies. Blow molding is a hybrid of injection and extrusion where hollow containers, such as bottles, are produced by forcing compressed air against the walls of molds in order to expand the molten PET.
Quality Control and Finishing
The current production of the PET plastics has advanced quality control protocols that include checking of the dimensions, testing of the barrier properties, and visual examinations. Often, surface treatments can be used to improve particular characteristics, including UV resistance or better printability. Last inspection is done to ensure products of high quality standards in the industry, and then they are distributed to the final consumer.
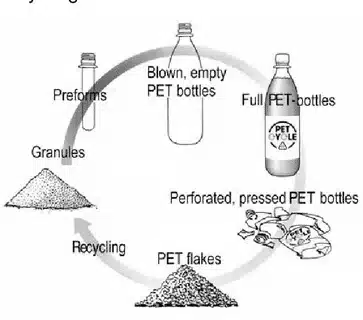
Recycling PET Plastic

Importance of PET Recycling
Recycling of PET plastic has great environmental impacts, as it will cut the waste in landfills and save the amount of natural resources used to make virgin plastics. It eliminates an estimated 1.8 billion pounds of PET plastic each year in the United States alone. Recycling PET plastic can save energy up to 84 percent over making new material, and also greatly lowers the amount of carbon emissions and impact on the environment.
Recycling Process Steps
The recycling process of PET plastic starts with collection and sorting, in which the automated systems eliminate the PET containers from others due to the density-based separation and optical recognition technology. Removal of contamination entails washing systems that remove labels, adhesives, and leftover material to make materials pure.
Cleaned PET plastic is shredded into flakes by mechanical recycling, and further washed and quality tested. The flakes may be melted down and reused to create other products or into polyester fibers to make textiles. A new technology known as chemical recycling disintegrates PET plastic into molecular components, which could be used to produce virgin-quality material using the recycled material.
Overcoming Recycling Challenges
To enhance the level of PET plastic recycling, the contamination challenges should be addressed with improved educational levels of consumers and increased collection procedures. The higher sorting equipment is technologically, the greater the recovery efficiency is achieved at lower processing costs. Extended producer responsibility programs also provide manufacturers with incentives to develop more recyclable PET plastic goods and assist in the development of recycling facilities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon Footprint Analysis
Production of PET plastics results in a CO2 equivalent of about 2.3 kg of CO2/kg material, which happens mainly through the energy-consuming polymerization process and extraction of raw materials. Nevertheless, the lightweight characteristics of the material minimize transportation emissions as opposed to glass substitutes. PET plastic recycling can up to 79% reduce the total carbon footprint, hence closed-loop systems are essential to environmental sustainability.
Waste Management Considerations
PPET plastic waste management needs a developed system of collection, good sorting infrastructure, and involvement of consumers in the system of recycling plastics. Non-recyclable PET plastic can be incinerated using energy recovery to produce electricity, but this process also releases CO2 emissions. The least preferable is the landfill disposal, which is a method that PET plastic does not biodegrade, thus taking up space.
Sustainable Practice Implementation
By adding more content of recycled PET plastic products into new products, the demand for virgin material is reduced, and the performance is maintained. Design to recycle principles push manufacturers to avoid using problematic additives and to make product structures in such a way that they become easier to process. Bio-based PET plastic production with renewable feedstock is a research area under the category of alternative materials because it can potentially lessen the environmental impact of materials by not compromising their material properties.
Education of consumers on appropriate recycling behaviors is conducted, and use reuse where necessary. Corporate sustainability programmes set high levels of recycled content goals and contribute to the development of recycling infrastructure. The economic incentive to better PET plastic management is established through government policies, such as bottle deposit and plastic waste reduction requirements.
Conclusion
PET plastic is one of the most versatile and significant materials of modern manufacturing that performs important functions in the packaging, textile, and many other specialized applications and provides its own benefits in durability, transparency, and recyclability. Although the environmental issues of non-biodegradability and pollution cannot be ignored, the fact that the material can be fully recycled, and it is possible to implement the concept of the circular economy, opens opportunities to use it more sustainably.
Knowledge of the properties, advantages, and disadvantages of PET plastic in the hands of consumers and manufacturers can help them make better choices that are both functional and environmentally friendly. With the evolution of recycling technologies and the growth of such sustainable practices, the PET plastic will have a chance to remain needed by society and cause the least harm to the environment.
We also urge the reader to engage in the recycling of PET plastics through plastic recycling schemes, use products with recycled content where available, and keep up with the development of alternative products that are sustainable. To get even more information about sustainable materials and recycling, read our guides on the principles of the circular economy and the latest technologies of biodegradable plastics.





