Learn the main distinctions between anodizing and plating, where each process is best used, and which one is the best process to use for your metal finishing.
Introduction
Two processes prevail in the metal finishing world: anodizing and plating. And yet, which of these really excels? These methods are essential to understand by industries in aerospace to consumer electronics, where a surface treatment can determine the performance and durability of a product. This is a guide to the depths of the differences, advantages, and uses of anodizing and plating, and it will guide you in making knowledgeable choices regarding your metal finishing requirements.
What Are Anodizing and Plating?
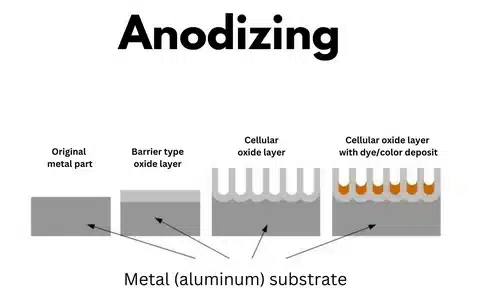
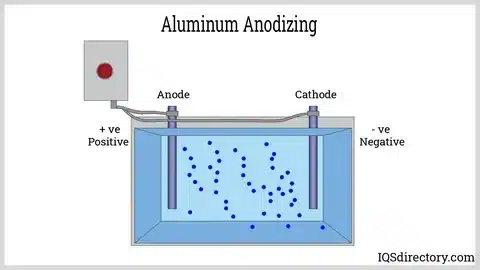
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enriches the oxide layer that naturally exists on the surface of metals, mostly aluminum. In this process, metal is used as the anode in an electrolytic cell, resulting in the production of a tough layer of oxide, which is part of the base material. It is a controlled oxidation that forms a protective layer whose properties have considerable support for the natural properties of the metal.
Plating
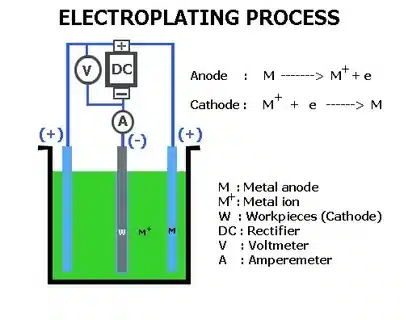
Electroplating or plating is a process in which a metal is plated onto a surface by means of electrochemical plating. Here, the object is a cathode, and the ions of a metal solution are reduced on the object, forming a uniform, but thin, coating of another metal, such as nickel, chrome, gold, or copper.
Key Differences Between Anodizing and Plating
| Feature | Anodizing | Plating |
| Process Type | Electrochemical oxidation | Electrochemical reduction |
| Coating Material | Oxide of the base metal | A different metal (e.g., nickel, chrome) |
| Durability | Highly durable and wear-resistant | Varies; can be less durable than anodizing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially for aluminum alloys | Good, depending on the plating material |
| Aesthetic Options | Limited; typically matte finishes | Wide range; glossy, metallic finishes |
| Environmental Impact | Generally eco-friendly; minimal toxic byproducts | Can produce hazardous waste; requires careful disposal |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Anodizing
Advantages:
- Improved corrosion and wear resistance durability, in the order of decades.
- The capacity to color and stain the oxide layer to be pretty.
- A clean and eco-friendly process with minimal waste.
- It is dimensionally accurate because the coating expands out of the base material.
- Good insulation characteristics with electricity.
Disadvantages:
- Reduced to metals that are capable of forming a stable oxide surface (mostly aluminum and titanium).
- Surface finish is matte with minimum gloss choices.
- There is a limitation in color options as compared to plating.
- Increased costs of setting up specialized anodizing equipment.
Plating
Advantages:
- A large variety of aesthetic finishes, such as mirror-bright and ornamental.
- Applicable to most types of metals, such as steel, copper, and brass.
- Greatly improves conductivity where conductive plating material is utilized.
- Reduced the costs of equipment used in simple plating processes.
- Selectivity to plate individual localities.
Disadvantages:
- Possibility of corrosion with time, particularly when the coating is destroyed.
- Environmental issues because the chemicals being toxic, and heavy metals.
- Wear or chipping can result in the exposure of the underlying material.
- Needs special care in waste management and disposal.
Which Process Is Right for Your Application?
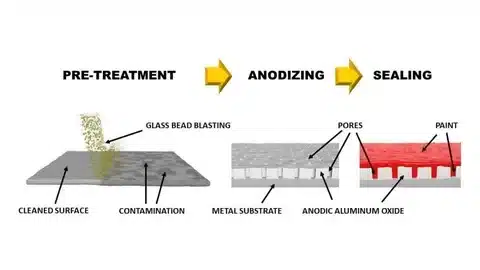
Choose Anodizing for:
- Uses of outstanding durability and corrosion resistance.
- Parts that are exposed to severe weather or used in ocean use.
- Long life is important in aerospace, automotive, and architectural environments.
- Projects in which environmental impact is a major issue.
- Components that require the property of electrical insulation.
Choose Plating for:
- Uses that emphasize the look and ornamentation finishes.
- Electronic components that require a higher conductivity.
- Products that need appearance to sell best, such as jewelry, hardware, and consumer goods.
- Projects that have budget limitations and an initial cost a key factors.
- Articles that needed definite metallic features (hardness, magnetism, and so on).
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Anodizing is normally viewed as being environmentally friendly, particularly in cases where non-toxic electrolytes are employed. Little hazardous waste is generated in the process, and the oxide layer formed is non-toxic and chemically stable. A majority of the anodizing solutions are recyclable or neutralizable.
Plating may include dangerous chemicals such as heavy metals, acids, and cyanides. This is to be done with proper disposal and safety, such as specific waste treatment facilities, and safety gear among the personnel. Nevertheless, more sustainable as they develop as eco-friendly plating chemistries, making some processes more sustainable.
Conclusion
Metal finishing has special advantages in both anodizing and plating. Anode is better in durability, corrosiveness, and is environmentally friendly, thus suitable for long-term application where performance is the most important. Plating offers better aesthetic possibilities and flexibility in a range of metals, suitable for decorative and electronic uses. The decision is then based on your personal needs, such as durability, aesthetics, environmental issues, and cost factors. Use a metal finishing expert to help identify the best process to use in your specific application and achieve optimum outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can anodizing be applied to steel? No, anodizing is mostly applied to aluminum and other non-ferrous materials such as titanium. Steel has an alternative surface coating of phosphating or powder coating with similar protection benefits.
2. Is plating more cost-effective than anodizing? Depending on the applications, costs differ a lot. Plating may be cheaper when used as decoration and for small volumes of production, whereas anodizing may be a better long-lasting investment as it is both more durable and needs less maintenance.
3. Can anodized surfaces be repaired? Anodized surfaces are very strong and hardly in need of repair. Nevertheless, in case of damage, localized damage can be repaired by stripping and re-anodizing to restore it completely, but such a situation is only common in case of extreme mechanical damage.





