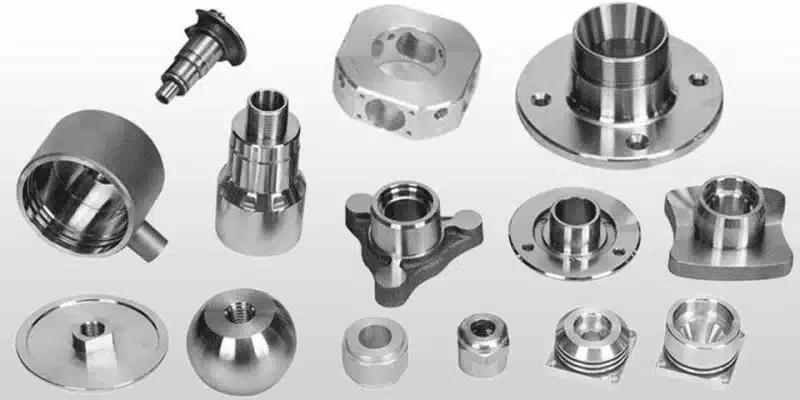
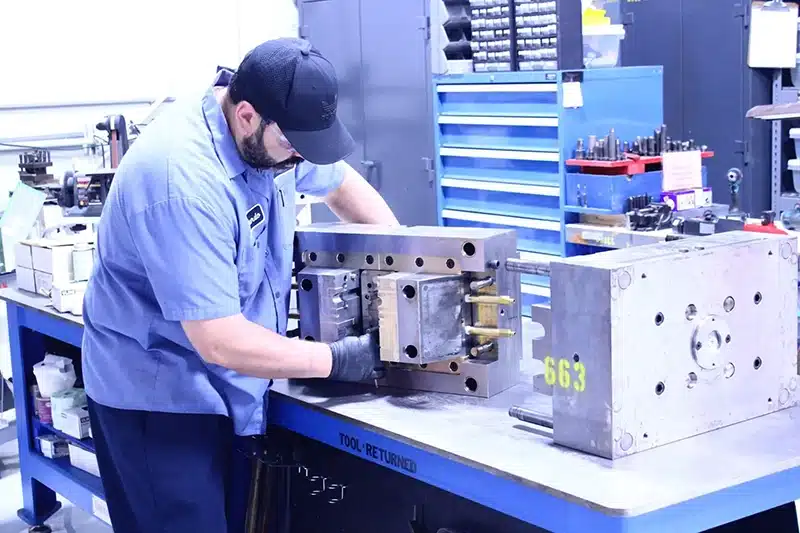
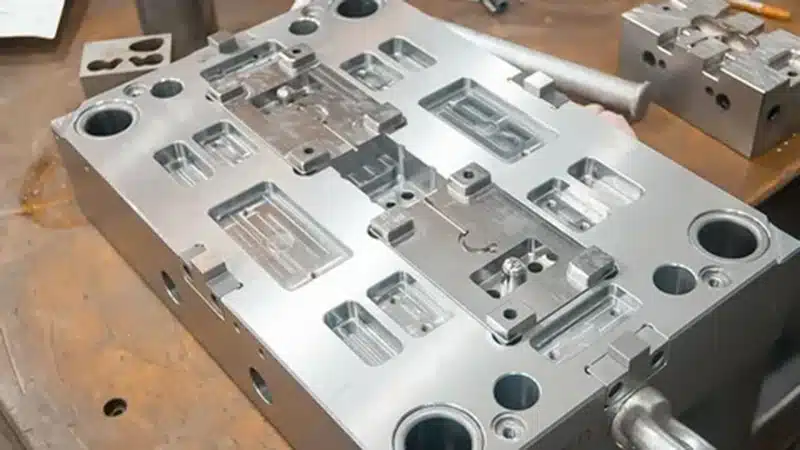
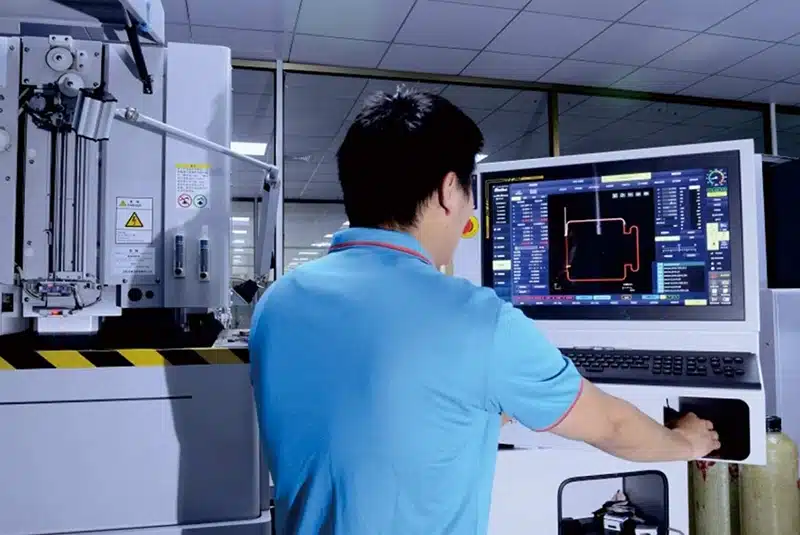
Why OEMs Prefer Long-Term CNC Machining Partners for Mold Components
OEMs opt for long-term CNC machining partners for mold components to leverage accumulated expertise, ensuring consistent tolerances and reduced variability. This article examines the benefits of collaboration, from engineering alignment to stable injection molding outcomes, highlighting why switching suppliers often backfires.