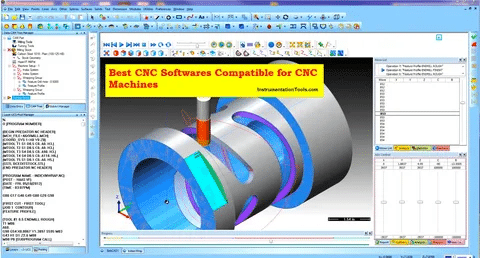
Introduction
The modern manufacturing industry was transformed by the introduction of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machine since it oversees the production of precision pieces with impressive precision and reproducibility. Underlining all computerized numerically controlled endeavors is the advanced software that figures out how digital designs turn into specific machine actions. Among precision mold component makers, automotive connectors makers and medical device parts manufacturers, learning about CNC software is one of the keys to tight tolerances and high quality which is mandatory today in many industries.
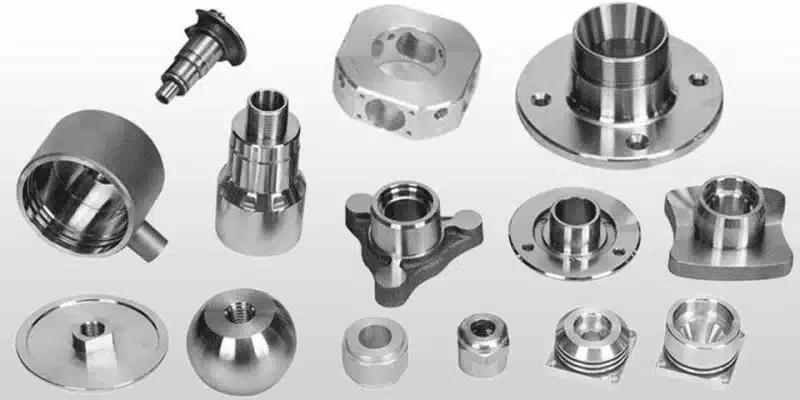
You may be cutting down on tungsten-steel components, or you could be producing complex parts of connector molds, but the proper CNC software can be the determining factor between achieving standards and not even reaching a level of quality. This guide is a complete overview of the types of CNC software out there and it brings everything together to allow you to make effective decisions in finding the best solution to your manufacturing environment.
What is CNC Software?
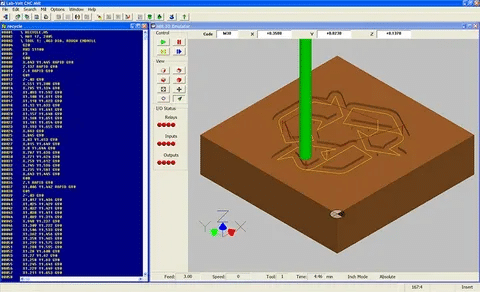
CNC software is the brain in the computer version of controlling the machine right in the initial phase of design to the final production stage. This software reads through computer-aided design (CAD) and translates them into G-code, the universal programming language that CNC machines read. The software is used to control the machining operations through the use of tool path motions, spindle speeds, feed-rates as well as coordinate-systems.
CNC software in the present day has been incorporated into designing processes that allow the manufacturers to easily transition between designing and production with minimal human interference. In case of precision manufacturing that includes things like semiconductor packaging components manufacturing or medical mold parts manufacturing, the software has to support non-trivial geometries with exceptionally high dimensional tolerances and requirements of surface quality.
Types of CNC Software

Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
CAD software designs the first forms of 3D models and technical illustrations which act as the guideline in the CNC machining. Through these programs, engineers are able to create detailed components as far as their proper size, geometrical tolerances, as well as their material composition. The high-end CAD software has simulation features that can reveal any possible manufacturing problem even prior to the production.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) Software

A CAM software is used to fill the gap between design and manufacturing, as it was able to extract the toolpaths and machine code with the CAD models. This software also computes optimal cutting methods, provides suitable cutting tools and machining parameters to reach required finishes and dimensional tolerance of the surface. With precision mold components, the CAM software should be able to perform intricate 3D surface and control the rate of material removal.
CNC Control Software
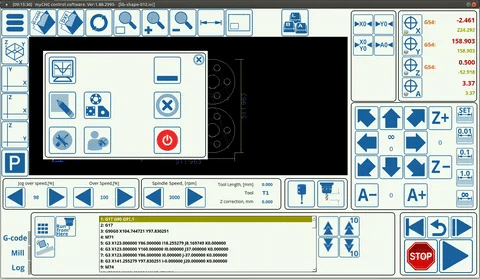
Control software is in charge of the actual CNC machine and reads pure G-code instructions and handles real-time operations on the machine. This computer program organizes various axes of motion, controls the state of cutting and activates security measures. Superior control software is fitted with adaptive machining software that tunes the parameters in accordance with real-time monitoring and sensor responses.
Simulation and Verification Software
Simulation programs mimic virtual simulation of machining processes which manufacturers use to detect any possible collision, confirm toolpaths, and streamline work cycles prior to actual work. One of the most useful components of this software is the use of complex components, such as automotive connector molds, because of the time and cost associated with trials and errors do not apply.
Best CNC Software for CNC Machines
Fusion 360
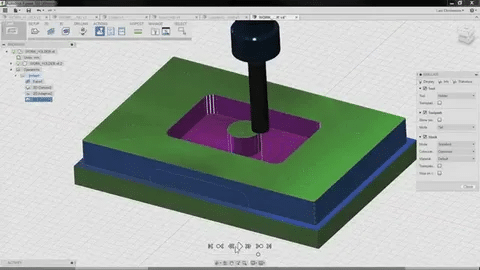
Autodesk Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD/CAM/simulation system that is specifically well-learned for precision manufacturing. This software is effective in creating smooth toolpaths in complex geometries and has more advanced options such as adaptive clearing and high speed machining strategy. Its embedded simulation environment assists manufacturers modify cutting parameters to minimize cycle times and also keep up the standard of surface quality.
AutoCAD
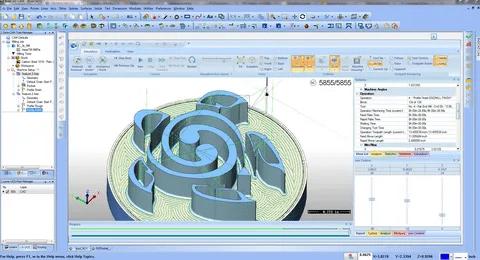
AutoCAD has continued to be a foundation of technical drawing and two-dimensional design, and also features dedicated toolsets to mechanical engineering. AutoCAD is a CAD solution although it is very compatible with most CAM packages and is very good when it comes to creating comprehensive technical illustration and documentation. It is also useful in the design of complex mold components that require intimate tolerances because of the precision drawing tools.
SolidWorks
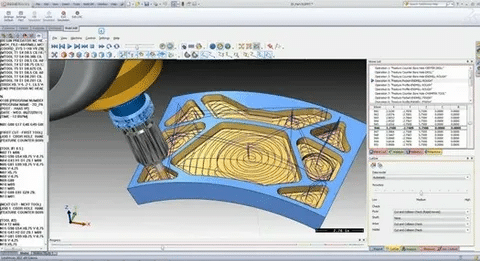
SolidWorks has all the features of 3D modeling with its specific modules of mold design and production. The software features sophistically surfacing tools necessary to generate complicated mold geometry and integrated simulations to prove a design prior to production. Its CAM software is very efficient in its application in precision machining where frequent surface finishes are necessary.
Inkscape
The Inkscape is a capable open-source tool, using 2 dimensional designing, and vector drawing, so it is appropriate to use Inkscape in laser cutting, engraving, or when the CNC requests simple processes. Although lacking the functionality of comparable commercial solutions, Inkscape offers affordable solutions to routine machining tasks and prototyping.
Easel
Easel is the consumer-friendly CAD/CAM software company that provides CNC fabricators with small-scale needs. The online service streamlines design-to-manufacture process and has inbuilt machine control capabilities. Easel may not be appropriate in precision manufacturing, but anyone who wants to get introduced to the concepts of CNC software will do well to start by using it.
Carbide Create
Carbide Create offers built-in CAD/CAM build to focus on small CNC machines and entry-level contingent CAD/CAM. The software has user-friendly design features and it provides solid toolpaths to simple machining tasks. It has an easy interface to use so that the user unfamiliar with CNC programming can use it but also enough functionality to build a prototype.
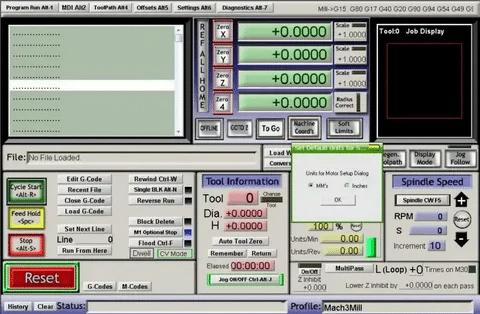
Mach3
Mach3 has established a name as a stability CNC control software solution, especially in retrofit and made-to-order machine building. The software offers full capabilities in machine control whereby it supports different types of motors and feedback systems. Its adaptability is that it can be used in specialized manufacturing applications that require the system of control to be specific and otherwise standard specified systems may fail to achieve the desired requirements.
LinuxCNC
LinuxCNC provides a free and open-source CNC controller with high real-time capabilities that are appropriate to precision manufacturing. The software accommodates the sophisticated machine configurations and offers a lot of customizations of specialized manufacturing needs. It is under an active community of developers who make it further improve and support emerging technologies.
GRBL
GRBL offers a lightweight CNC firmware control focusing on Arduino platforms and small CNC machines. Although GRBL is not intended to be applied to large-scale productions, it provides cost-efficient solutions to prototyping and small-scale productions. This open-source program can be customized to serve particular use of applications.
CAMotics
CAMotics is focused on CNC simulation and G-code checking and offers high-end visualization of complex manufacture tasks. The software assists manufacturers to determine potential problems in advance of production and optimally calculate toolpaths to make production more efficient. Its correct simulation environment comes in very handy in precision manufacturing processes where the cost of materials and set up time is a major concern.
Factors to Consider When Choosing CNC Software
Precision Requirements
Criteria that should determine software decision are the dimensional accuracy and the surface finish required on your components. When there is a need to manufacture precision mound parts with tight tolerances of less than 0.001 mm, then select software with detailed description of the toolpaths and well equipped geometric modeling. think about the software and the ability to process complicated 3D surfaces and presenting a constant cutting condition throughout the machining process.
Material Compatibility
Other materials need various machining plans and cutting programs. Check your preferred software to contain libraries of materials as well as cutting data suitable to your applications. The software needs to have support to newer methods of machining such as high-speed machining and trochoidal milling in the case of tungsten-steel components and tool steels that have been hardened.
Integration Capabilities
It is worth reflecting on the compatibility of the software in your established design/manufacturing processes. Identify solutions that are compatible with standard file formats that allows easy exchange of data with CAD systems, quality control systems and manufacturing execution systems. Integration features are especially significant in high volume manufacturing.
Scalability and Support
Check how much the software will support your manufacturing practice and the rate of technical support. Examples of the factors include costs of licensing, training needs and maintenance costs. In the case of precision manufacturing this is important because to ensure productivity and quality standards, stable technical support and regular software updates are needed.
Machine Compatibility
Verify the softwares compatibility with your cnc machine controllers and ensure that it is compatible to your specific feature and capabilities of the equipment. Think about such aspects as axes quantity, the types of spindles, and the options of machines. Ability to work with post-processors and special features of specific machines can affect productivity and user-friendliness in significant ways.
Conclusion
The choice of CNC software is essential to obtain the required level of precision, effectiveness, and quality that is typical in contemporary manufacturing. Software selection has a direct influence on how well you can comply with customer requirements and retain a competitive edge regardless of whether you are in the design phase or ready to manufacture. As a manufacturer of precision mold parts, connectors on automobiles, and parts on medical equipment, making a good investment is the purchase of involved software to maintain the quality products at all times and to accommodate future expansion.
The trend in the software environment is also trending towards the incorporation of cloud-based computing platforms, the use of artificial intelligence, and highly performing simulations. Be updated on the latest technological measures available and think on possible ways of achieving your manufacturing process with the use of new software and therefore the extended abilities you will have.
Being in the market of CNC software you should pay attention to the solution that will fit your concrete manufacturing needs and will show the required stability of performance and will be scalable enough in the future to allow meeting the expected growth. A wise investment in the right software will further be rewarded in better productivity, less scrap, and an increased capacity to satisfy more and more demanding customers as well.